Miki Ebisuya Group
Cross-species comparison and manipulation of the organoid zoo
© Humboldt Foundation
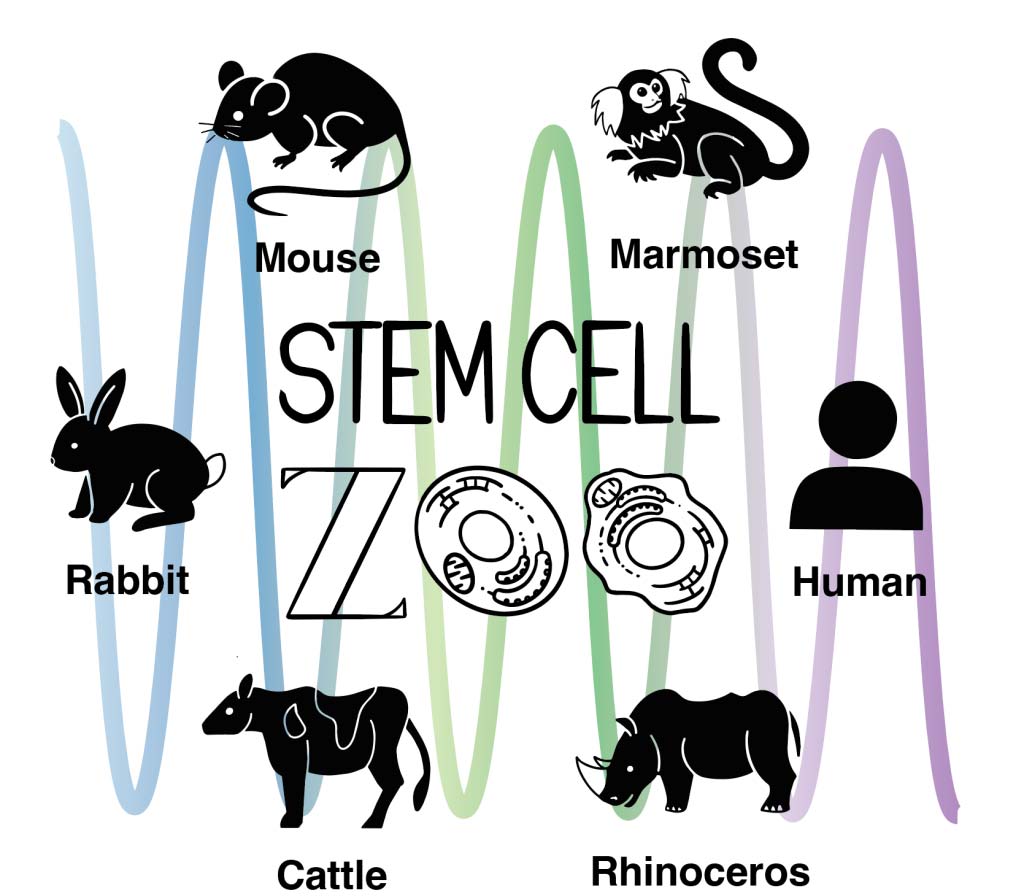
Different animal species exhibit different physiological times and different forms. For example, the human gestation period is about 9 months, compared to just 20 days for mice and almost 1.5 years for rhinoceroses. How organisms achieve the time and form inherent in these species is a fundamental question in biology and biophysics, but the mechanism remains largely unknown. One of the challenges of such studies is the difficulty to perform experiments on different animals, especially living embryos – we can’t keep rhinos in the lab. Therefore, our group uses pluripotent stem cells established from various animals, or the “stem cell zoo” (Fig. 1). By letting stem cells differentiate into appropriate cell types, we can recapitulate species-specific time, or create a tissue structure that partly mimics the morphology of developing embryos. These in vitro models created from the stem cell zoo not only enable the comparison of different species in similar culture conditions, but also have the advantage of being easy to quantitatively measure and experimentally manipulate. (see figure 1)
Species-specific biological time
We recently recapitulated the segmental clocks, the oscillatory gene expressions observed during animal development, from stem cells of mice, rhinos, and humans, finding that their oscillation periods were 2 hours, 4 hours, and 5 hours, respectively (Fig. 2). Interestingly, the reaction kinetics of the core segmentation clock gene, including the speeds of protein degradation and protein production, were also found to be unique to each species. So the cells of different species, despite their seemingly similar appearances, seem to know what animals they are. We are now investigating the mechanisms that achieve these species-specific segmentation clock periods and biochemical reaction kinetics. We also study another interesting example of species-specific biological time, the heart rate, using the stem cell zoo. (see figure 2)
Species-specific morphogenesis and mechanics
Even more complex 3D tissue structures, called organoids, can be created from the stem cell zoo. For example, we recently developed a novel human organoid that mimics periodic body segment formation observed during early development (Fig. 3). We plan to use such organoids to measure species-specific morphology and key biophysical parameters, such as kinetics, mechanics and metabolism. (see figure 3)
Manipulation of species-specific time and morphology
Once we identify the biophysical parameters controlling species-specific time and morphology, we want to manipulate them. If we can produce a mouse tissue that shows human-like time and shape, for example, that will be proof that we understood the mechanism of the species specificity. Although in vitro models derived from stem cells are amenable to experimental manipulation, tools for manipulation are still lacking. So we are also developing tools to manipulate stem cells and organoids. For example, we recently developed a new optogenetic tool to manipulate the shape of cells and tissues with light. (see figure 4)
Overall, cross-species comparison and manipulation of stem cell-derived models is a new field that is just beginning. While incorporating new technologies of measurement and manipulation, we will seek the universal mechanisms underlying species-specific time and morphology.
Future Projects and Goals
- Investigation of the biophysical mechanisms underlying species-specific biological time
- Investigation of the biophysical mechanisms underlying species-specific morphogenesis and mechanics
- Manipulation of species-specific time and morphology
Methodological and Technical Expertise
- Stem cell zoo (collection of stem cells of diverse mammalian species)
- Induction protocols of several cell types/organoids
- Quantitative measurements of biological rhythm and kinetic parameters
- Quantitative measurements of organoid morphogenesis
- Synthetic biology tools, including optogenetics